Exact Query Answer: When Should You Take Creatine?
Creatine can be taken before or after a workout, with benefits associated with both timings. Pre-workout creatine helps boost immediate energy and enhance performance during exercise, while post-workout creatine supports muscle recovery by replenishing depleted creatine stores. Consistent daily intake of 3-5 grams is crucial, as it ensures muscle creatine levels remain saturated, regardless of when it’s taken.
What is Creatine and How Does it Work?
Role of Creatine in Energy Production
Creatine plays an important role in the body’s production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary source of high intensity, short-duration exercises such as sprinting, weightlifting, or HIIT.
Indeed, it is stored in the muscle as phosphocreatine; therefore, replenishment occurs very rapidly when the demand for ATP is present. Increase in stores through supplementation enhances strength and power performance.
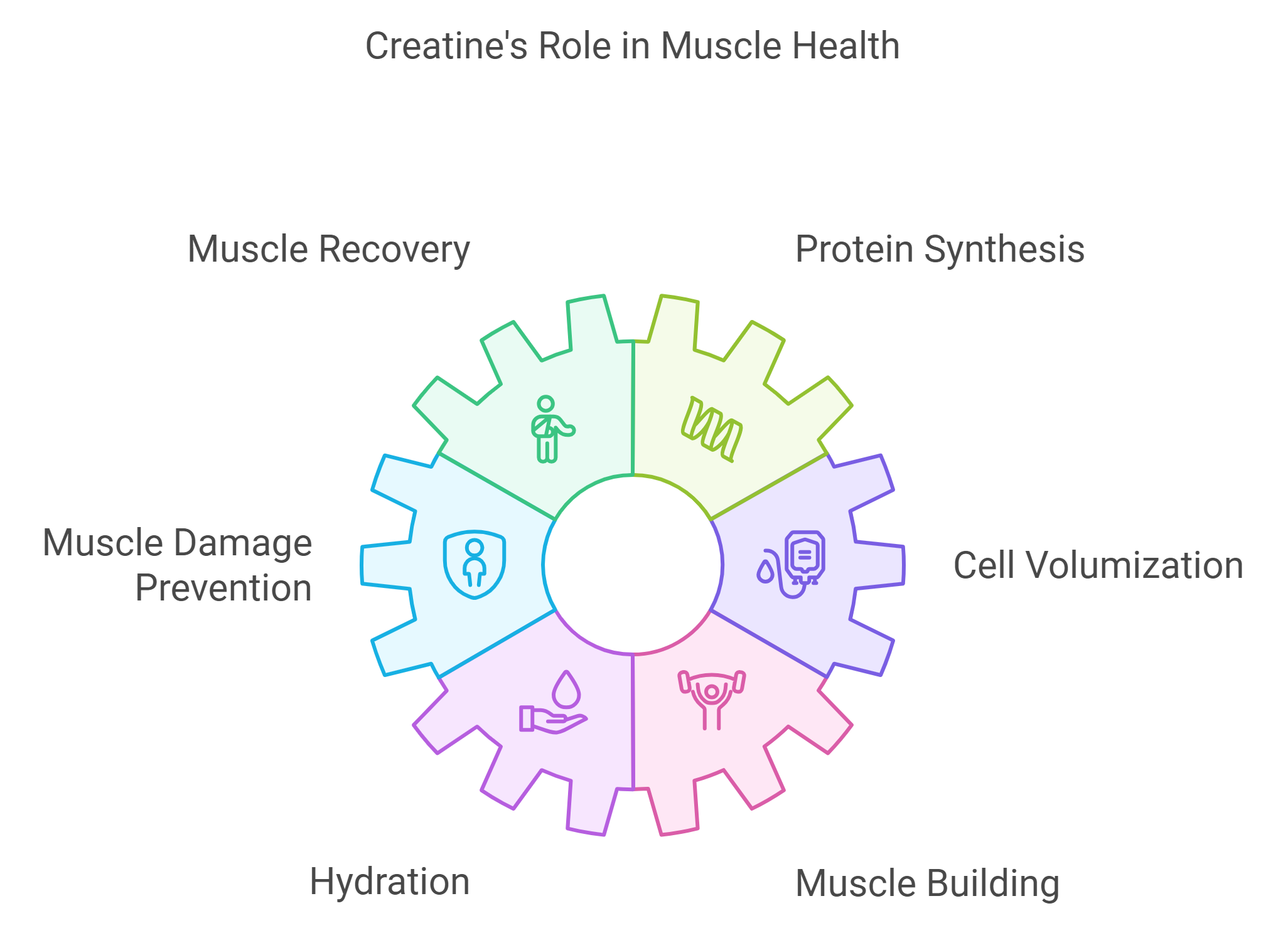
How Creatine Helps in Muscle Recovery and Building
Apart from its performance-enhancing properties, creatine also helps during muscle recovery by promoting protein synthesis of muscles and preventing muscle damage following exercises.
Moreover, it promotes cell volumization that ensures hydration inside the muscle cells. In the long run, this process results in the building of the muscles and faster times of recovery between workouts if the dose is taken appropriately.
When Would be the Right Time to Take Creatine?
Pre-Workout Creatine: Effects
Intake of creatine before exercise gives the benefit of fast energy supply. It can be particularly helpful with exercises requiring explosive power as well as endurance, like weightlifting or sprinting.
By increasing the pre-exercise phosphocreatine in the muscles, pre-exercise creatine helps you perform better in rapidly generating energy spikes that are needed for peak performance in high-intensity efforts.
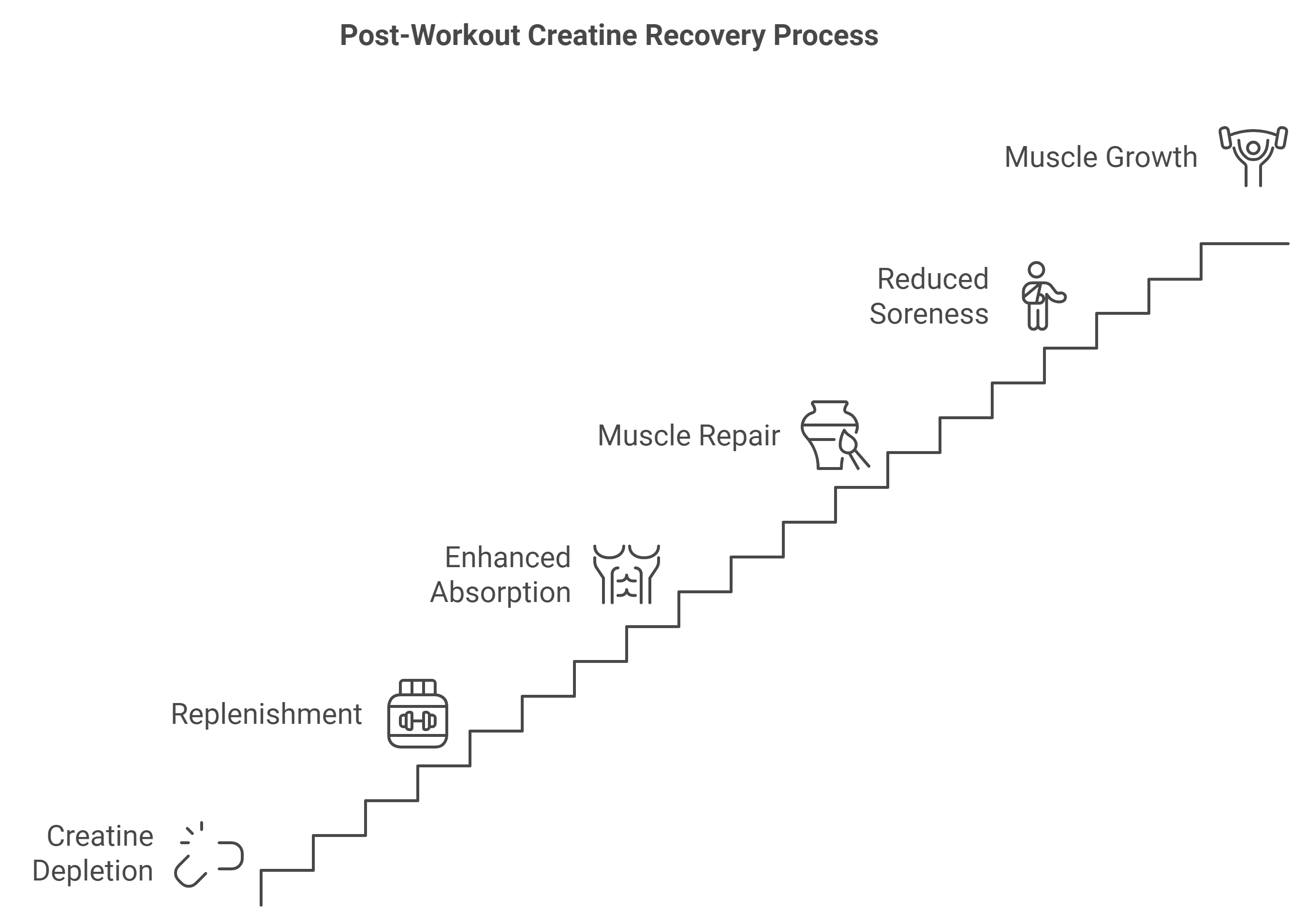
Post-Workout Creatine: Recovery Effects
Creatine taken post-workout confers certain advantages concerning the repair of muscles. During exercise, creatine stores within muscle fibers are depleted.
Replenishment of those after exercise enhances the repair of muscle tissue and the rate of recovery.
When supplemented with a protein or carbohydrate source, absorptive function of the muscle cells increases due to creatine, aiding in quicker repair and soreness of the muscles.
That is why the supplement is so often aimed at recovery and more muscle growth post-workout.
Consistency Counts: Dosage Needs Daily Basis
Though pre- and post-workout needs of creatine differ, what matters the most is consistency. At all times, when it comes to daily intake that reaches the desired saturation levels in the muscles, the other times of the day are covered. Whether before workout, after workout, or at any other time, 3-5 grams per day delivers the best to maximize the muscle creatine content for strength, endurance, and recovery (PhD Nutrition) (PhD Nutrition).
How to Use Creatine for Best Effectiveness
Loading Doses vs. Maintenance Doses
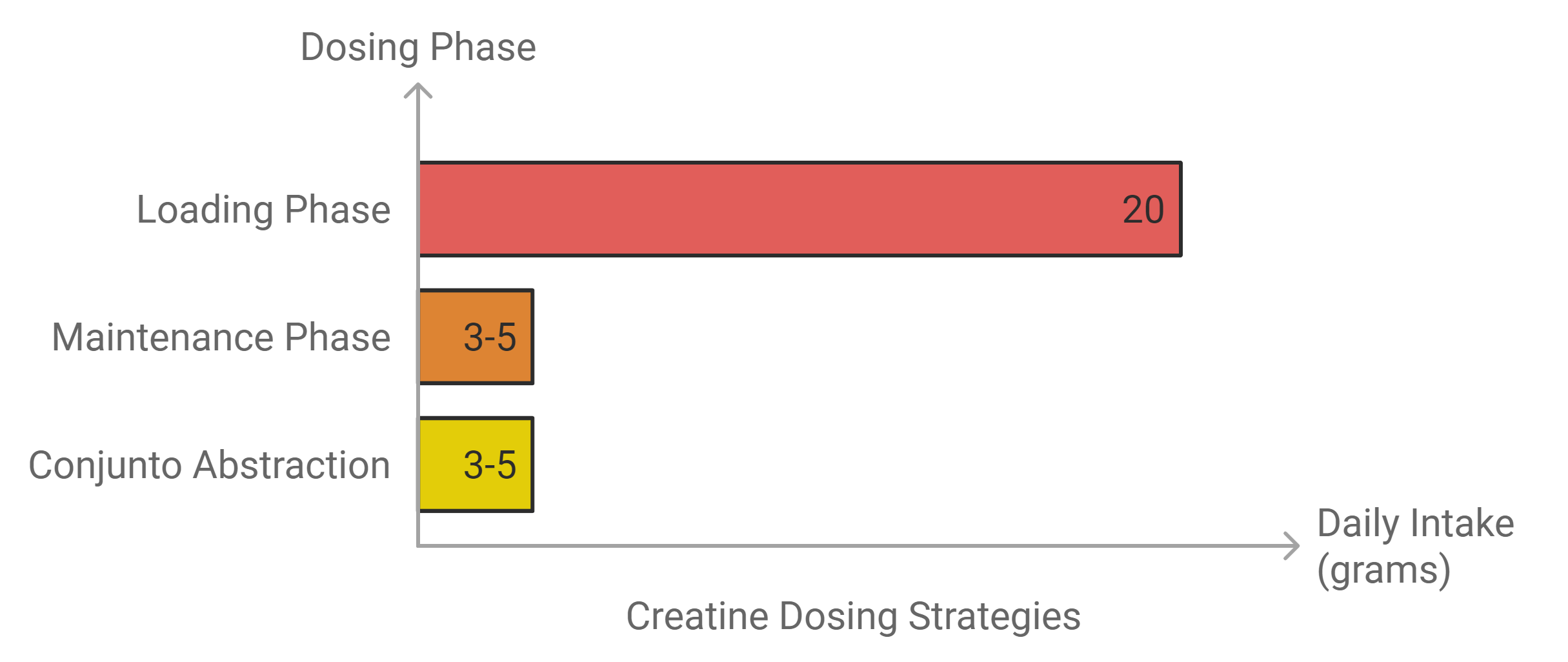
There are two main types of creatine intake: the loading phase and steady intake.
Loading Phase:
This is when 20 grams a day, taken as four 5-gram doses over 5 to 7 days, provides a rapid loading of muscle creatine stores; then a maintenance dose is taken at 3 to 5 grams per day.
Conjunto Abstraction:
Avoid the loading phase entirely and must consume 3-5 grams daily from day one. This makes it so that the outcome is as effective, but takes longer for maximum saturation(PhD Nutrition).
Both are quite effective. The loading phase does provide some quick initial results, but long-term outcome comparison is similar regardless of what method is used.
Should you Stack Creatine with Other Supplements?
Creatine could be combined with some other supplements, like proteins or BCAA, to enhance the recovery as well as the muscle building.
However, some research indicates that creatine supplementation with carbohydrates enhances the intake of creatine in the muscles and therefore might make a decent addition to a shake following a workout.
Although creatine can go along with caffeine, care should be taken since some studies show that caffeine exerts an inhibitory effect on creatine(PhD Nutrition).
Frequently Asked Questions
What time should I take creatine, pre or post exercise?
Creatine can be used both before and after workout. The pre-workout period is taken by the patient for him to put up a good performance, and then there is post-workout when the patient takes it up as a way of recuperating.
Do I take creatine on my days off?
Yes, the patient needs to take creatine during rest days too because it ensures that the muscles have elevated levels of creatine throughout, thus giving benefits continuously with time.
Will creatine make me gain weight?
Creatine will initially have an effect on water weight as the muscles retain more water. This is a temporary effect and mostly on muscle mass, not fat.
Do I need to “load” with creatine?
There’s no need to load your muscles with creatine. Increases saturation of the muscles but isn’t necessary; the body will build the same effect over time with daily intake of 3-5 grams.
How much water do I need to drink when on creatine?
Taking creatine will require substantial hydration, and maintaining fluid balance so that individuals do not cramp or become dehydrated due to the resultant retention of water within the muscles.

